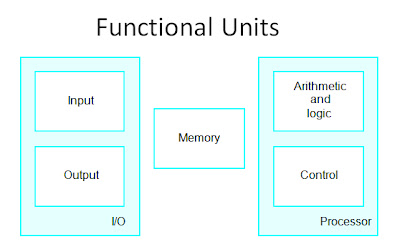
Objective Questions Computer Programming
1)What is the mean of type casting? Ch-7
a. Conversion of the Data item
b. Conversion of variables
c. fixed the value of Data item
d. none
Ans :
a
2) A nibble corresponds to Ch-2
a. 4 bits
b. 8 bits
c. 16 bits
d. 32 bits
Ans :
a
3) Which one is not logical operator? Ch-2
a. &
b. &&
c. ||
d. !
Ans :
a
4) Which one Keyword used to calling function back again and again? Ch-4
a. switch
b. goto
c. go back
d. return
Ans:
d
5) What will be the output of the following statement ? Ch-2
printf("%X%x%ci%x",11,10,'s',12);
a) error
b) basc
c) Bas94c
d) none of these
Ans :
b
6)What will be the output of printf("\\n"); Ch-2
a. \n
b. \\n
c. error
d. none
Ans :
a
7)What is the result of 16>>2? Ch-7
a. 4
b. 8
c. 3
d. 0
Ans :
a
8)What will be the output of following program Ch-2
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char letter =`Z`;
printf("\n%c",letter);
}
a. Z
b. 90
c. Error
d. Garbage Value
Ans :
a
9) What will be the result of the following code? Ch-5
#define TRUE 0
while(TRUE)
{
printf(“Wipro-BITS”);
}
printf(“BITS PILANI”);
a.Wipro-BITS
b.Nothing will be printed
c.BITS
d.BITS PILANI
Ans :
d
10) What will be the output of following program Ch-2
main()
{
int x=5;
printf(“%d,%d,%d\n”,x,x< <2,x>>2);
}
a. 5,19,1
b. 5,20,1
c. 5,21,1
d. 5,20,1
Ans :
b
11). What will be the output of the following arithmetic expression ? Ch-2
5+3*2%10-8*6
a) -37
b) -42
c) -32
d) -28
Ans :
a
12). What will be the output of the following statement ? Ch-2
int a=10; printf("%d &i",a,10);
a) error
b) 10
c) 10 10
d) none of these
Ans :
d
13) What will happen if in a C program you assign a value to an array element whose subscript exceeds the size of array? Ch-8
a. The element will be set to 0
b. The compiler would report an error
c. The program may crash if some important data gets overwritten
d. The array size would appropriately grow
Ans :
c
14). What will be the output of the following statements ? Ch-8
int x[4] = {1,2,3}; printf("%d %d %D",x[3],x[2],x[1]);
a) 03%D
b) 000
c) 032
d) 321
Ans :
c
15) output ?
int testarray[3][2][2] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
What value does testarray[2][1][0] in the sample code above contain? Ch-8
a) 11
b) 7
c) 5
d) 9
Ans :
a
16) What is the output of this program? Ch-2
main()
{int a=-3;a=-a-a+a;printf("%d",a);
}
a. error
b. compilation failed
c. 3
d. none
Ans :
c
17) How many time while loop will executed? Ch-6
int main()
{
int j=1;
while(j <= 255)
{
printf("%c %d\n", j, j);
j++;
}
return 0;
}
a. error
b. 255 times
c. 200 times
d. 250 times
Ans :
b
18)output ?
int z,x=5,y=-10,a=4,b=2; Ch-2
z=x++ - --y*b;
a.5
b.6
c.10
d.11
Ans:
c
19)output ? Ch-2
int a=10,b;
b=a++ + ++a;
printf(“%d,%d,%d,%d”,b,a++,a,++a);
a.12,10,11,13
b.22,10,11,13
c.22,11,11,11
d.22,13,13,13
Ans :
d
20) What will be output when you will execute following c code? Ch-4
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
int a=5,b=10,c=1;
if(a&&b>c){
printf("cquestionbank");
}
else{
break;
}
}
a. cquestionbank
b. It will print nothing
c. Run time error
d. Compilation error
Ans :
d
21)What is the output? Ch-4
void main()
{
int a=10,b=20;
char x=1,y=0;
if(a,b,x,y)
{
printf("EXAM");
}
}
a. XAM is printed
b. exam is printed
c. Compiler Error
d. Nothing is printed
Ans :
d
22)What will be the output Ch-8,9
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[7]=”Network”;
printf(“%s”,arr);
return 0;
}
a.Network
b.N
c.Garbage value
d.Compilation error
Ans :
c
23)What will be output of the following program Ch-2
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int i=5,j;
j=++i+++i+++I;
printf(“%d %d”,I,j);
return 0;
}
a.7 21
b.8 21
c.7 24
d.8 24
Ans :
d
24)What will be output of following c program Ch-2,7
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int class = 150;
int public =25;
int private=30;
class = class>>private-public;
printf(“%d”,class);
}
a)1
b)2
c)4
d)Compilation error
Ans :
c
25)What will be output of c code Ch-2,5
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=2,j=2;
while(i+1?—i:j++)
printf(“%d”,i)
return 0;
}
a)1
b)2
c)3
d)4
Ans :
a
26) What will be output when you will execute following c code? Ch-4
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
int a=100;
if(a>10)
printf("M.S. Dhoni");
else if(a>20)
printf("M.E.K Hussey");
else if(a>30)
printf("A.B. de villiers");
}
a.M.S. Dhoni
b.A. B. de Villiers
c.M.S. Dhoni M.E.K Hussey A.B. de Villiers
d.Compilation Error
Ans :
a
27) What will be output when you will execute following c code? Ch-4
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
int a=5,b=10;
if(++a||++b)
printf("%d %d",a,b);
else
printf("John Terry");
}
a.5 10
b.6 11
c.6 10
d.5 11
Ans :
c
28) What will be output when you will execute following c code? Ch-4
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
int a=5,b=10;
if(++a||++b)
printf("%d %d",a,b);
else
printf("John Terry");
}
a.It will print Memento at one time
b.It will print Memento at three times
c. It will print Memento at ten times
d.It will print Memento at infinite times
Ans :
d
29) what will be output when you will execute following c code? Ch-4
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
int const X=0;
switch(5/4/3){
case X: printf("Clinton");
break;
case X+1:printf("Gandhi");
break;
case X+2:printf("Gates");
break;
default: printf("run time error");
}
}
a.Clinton
b.Gandhi
c.Gates
d.Compilation error
Ans :
d
30) What will be output when you will execute following c code? Ch-4
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
switch(5||2|1){
case 3&2:printf("Anatomy of a Murder");
break;
case -~11:printf("Planet of Apes");
break;
case 6-3<<2:printf("The conversation");
break;
case 5>=5:printf("Shaun of the Dead");
}
}
a.Anatomy of Murder
b.Planet of Apes
c.The conversation
d.Compilation error
Ans:
d